デザインパターン Iterator:1つずつ数える
目次
概要
配列系データからデータを取得するデザインパターン。
hasNext()とnext()メソッドだけを実装し、
データ構造を見せない(index番号等を引数に渡さない)。
配列におけるindexの開始値や終了値の認識の違いによるミスを防げる。
クラス図
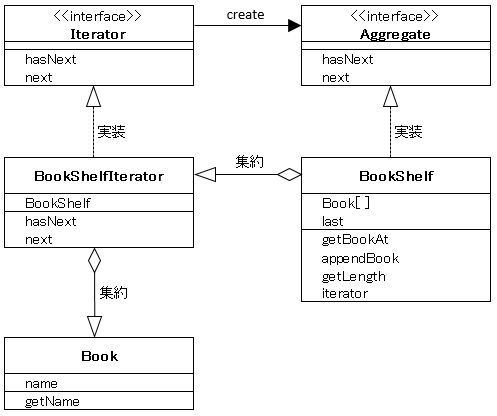
集約:別クラスのインスタンスをメンバーに持つ事。
「オブジェクト指向: UML(クラス図)/集約」参照
コード
反復子インターフェイス(Iterator)
public interface Iterator {
public abstract Boolean hasNext();
public abstract Book next();
}
集合体インターフェイス(Aggregate)
public Iterator iterator();
}
反復子クラス(BookShelfIterator)
private BookShelf bookShelf_;
private int index_;
public BookShelfIterator(BookShelf bookShelf){
this.bookShelf_ = bookShelf;
this.index_ = 0;
}
public Boolean hasNext(){
if (this.index_ < this.bookShelf_.getLength()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
public Book next(){
Book book = this.bookShelf_.getBookAt(this.index_);
this.index_ ++;
return book;
}
}
集合体クラス(BookShelf)
private Book[] books_;
private int last_;
public BookShelf(int maxSize){
this.books_ = new Book[maxSize];
}
public Book getBookAt(int index){
return this.books_[index];
}
public void appendBook(Book book){
this.books_[this.last_] = book;
}
public int getLength(){
return this.last_;
}
public Iterator iterator(){
return new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
}
集合体で扱う要素(Book)
private String name_;
public Book(String name){
this.name_ = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name_;
}
}
イテレータの利用
import myIterator.Book;
import myIterator.BookShelf;
import myIterator.Iterator;
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book book1 = new Book("C#");
Book book2 = new Book("VB.NET");
Book book3 = new Book("JAVA");
Book book4 = new Book("JavaScript");
Book book5 = new Book("Perl");
BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(5);
bookShelf.appendBook(book1);
bookShelf.appendBook(book2~5);
Iterator it = bookShelf.iterator();
if ( it.hasNext() ){
Book book = it.next();
System.out.println(book.getName());
⇒ C#, VB.NET, JAVA, JavaScript, Perl
}
※ ↓ でも同じ動作をする。
しかし↑ はBookShelfIteratorがカプセル化されている事で、
よりクラス間の結合が弱く、汎用性が高くなっている。
BookShelfIterator bookShelfIterator(bookShelf);
if ( bookShelfIterator.hasNext() ){
Book book = bookShelfIterator.next();
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
}


